FOUNDATIONS
Other Chapters
FOUNDATIONSWALLSFLOORSROOFSDOORS AND WINDOWSSTAIRSSHORING, SCAFFOLDING & UNDERPINNINGWORKING DRAWINGS
- Q1: Define Foundation.Ans: The lowest part of a structure that transfers the load of the building safely to the soil below is called Foundation or Sub-structure.
- Q2: Enlist types of foundation.Ans: Some of the types are:
- ➔ Shallow Foundation
- ➔ Deep Foundation
- Q3: Define a shallow foundation.Ans: A foundation placed at a shallow depth (less than 3 meters), used when the soil has sufficient bearing capacity near the ground surface.
- Q4: Define a deep foundation.Ans: A foundation constructed at a greater depth (greater than 3 meters) when surface soil cannot support loads; examples include pile, pier, and caisson foundations.
- Q5: Differentiate between shallow foundation and deep foundation.Ans:
Shallow: Depth <= width, suitable for good surface soil.
Deep: Depth > width, suitable for weak surface soil requiring load transfer to deeper strata. - Q6: Enlist four purposes of foundation providing underground.Ans: Following are some purposes:
- ➔ Transfer building load to soil
- ➔ Prevent settlement
- ➔ Provide stability against sliding/overturning
- ➔ Distribute loads uniformly
- Q7: Enlist types of spread foundation.Ans: The types are:
- ➔ Wall footing
- ➔ Column footing
- ➔ Combined footing
- ➔ Raft/Mat foundation
- Q8: Define grillage foundation.Ans: A type of foundation using layers of steel or timber beams to distribute heavy loads over a large area at shallow depth is called Grillage foundation.
- Q9: Write about raft foundation.Ans: A large concrete slab covering the entire area beneath a structure, used when loads are heavy or soil has low bearing capacity is Raft foundation.
- Q10: Define stepped foundation.Ans: A foundation provided in steps on sloping ground to maintain the level of the structure is called Stepped foundation.
- Q11: Give a traditional formula to determine the width of the foundation.Ans:

- Q12: Write Rankine formula for determining depth of foundation.Ans:
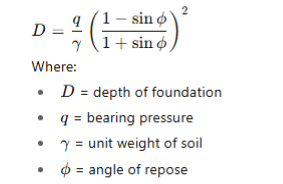
- Q13: Write formula to determine depth of concrete block in design of foundation.Ans:
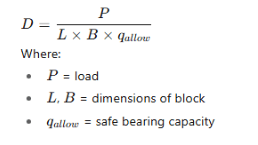
- Q14: What is the bearing capacity of soil?Ans: The maximum load per unit area that soil can safely carry without shear failure or excessive settlement is called bearing capacity of soil.
- Q15: Define ultimate bearing capacity of soil.Ans: The maximum pressure soil can withstand before failure occurs is called the ultimate bearing capacity of soil.
- Q16: Define safe bearing capacity of soil.Ans: The maximum pressure that can be safely applied to soil considering the factor of safety is called safe bearing capacity of soil.
- Q17: Define sub soil investigation.Ans: The process of studying soil properties, stratification, and groundwater conditions below the surface before construction.
- Q18: Give purpose to soil investigation.Ans: Soil investigation is done to:
- ➔ Determine soil bearing capacity
- ➔ Classify soil type and properties
- ➔ Locate groundwater table
- ➔ Ensure safe and economical foundation design
- Q19: Write methods of boring.Ans: Some methods are:
- ➔ Auger boring
- ➔ Wash boring
- ➔ Percussion boring
- ➔ Rotary boring
- Q20: Why is the bearing capacity of soil determined?Ans: To ensure the soil can safely support structural loads without risk of failure or excessive settlement.
- Q21: Enlist some causes of failure of foundation.Ans: Some of the causes are:
- ➔ Unequal settlement of soil
- ➔ Earthquakes
- ➔ Transpiration of trees and shrubs
- ➔ Poor quality material
- ➔ Lateral load of superstructure
- Q22: Name methods to determine bearing capacity of soil in the field.Ans: The methods are:
- ➔ Plate load test
- ➔ Standard penetration test (SPT)
- ➔ Cone penetration test (CPT)
- ➔ Vane shear test
- Q23: Define Isolated Footing.Ans: Isolated footings are used to support one column only.
- Q24: Define Combined Footing.Ans: Combined footings are used to support two columns. These footings are made when the distance between the columns is very small.
- Q25: Name the loads on foundation.Ans: Foundations bear the following loads:
- ➔ Dead Load
- ➔ Live Load
- ➔ Wind Load
- ➔ Self Load
- Q26: Name some types of Pile foundations.Ans: Some of the types are:
- ➔ Wooden Pile
- ➔ RCC Pile
- ➔ Concrete Pile
- ➔ Bearing Pile
- ➔ Fraction Pile
- Q27: What is the other name of Raft Foundation?Ans: Raft foundation is also known as Matt Foundation.
- Q28: Define Frame structure.Ans: A structure that has beams and columns to support the load and walls are non-load bearing.
- Q29: Define Grade Beam.Ans: A grade beam is a reinforced concrete beam that is constructed at ground level (or slightly below) and supports a wall by distributing its load to spaced foundations such as pile caps or caissons.
- Q30: Define Plinth Beam.Ans: A plinth beam is a reinforced concrete beam constructed at the plinth level (just above ground level) to support walls and prevent differential settlement.
- Q31: Define Joist.Ans: A joist is a horizontal structural member used in framing to span an open space, often between beams, and to support a floor or ceiling.
- Q32: Define Cantilever Footing.Ans: It is a type of foundation that extends horizontally to support a load without external support on one side.
