STRAIN
Other Chapters
STRESSSTRAINELASTICITYCENTER OF GRAVITYMOMENT OF INERTIASHEAR FORCE & BENDING MOMENTSOIL MECHANICSDEFLECTION IN BEAMSDESIGN OF BEAM & LINTELDESIGN OF RCCDESIGN OF RCC COLUMN & FOOTINGDESIGN OF RCC STAIRS
- Q1: Define Strain.Ans: The ratio of change in dimension to original dimension is strain. It has no unit.

- Q2: Why does strain has no unit?Ans: It is because both change in length and length have the same units which cancel out each other.
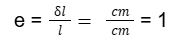
- Q3: Name the types of strainAns: The types are:
- ➔ Direct Strain
- ➔ Tensile Strain
- ➔ Compressive Strain
- ➔ Shear Strain
- ➔ Volumetric Strain
- ➔ Linear Strain
- ➔ Lateral Strain
- ➔ Direct Strain
- Q4: Define tensile strain.Ans: If a Tensile force is applied on the body and its length increases, this is a Tensile Strain.

- Q5: Define compressive strain.Ans: If a Compressive force is applied on the body and its length decreases, this is a Compressive Strain.
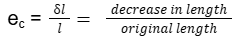
- Q6: What do you know about shear strain.Ans: The strain produced in a body due to Shear Force and Shear Stresses is called Shear Strain.
- Q7: Define volumetric strain.Ans: If a force is applied on the body and the volume of the body changes i.e. the length, height or width changes then such a strain is volumetric strain.
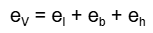
- Q8: Name various elastic constants.Ans: Some of the elastic constants are:
- Modulus of Elasticity
- Modulus of Rigidity
- Bulk Modulus of Elasticity
- Q9: Define Bulk Modulus of Elasticity.Ans: The ratio of direct stress to volumetric strain is Bulk Modulus.
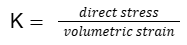
- Q10: Define Shear Modulus.Ans: The ratio of shear stress to shear strain is Shear Modulus.
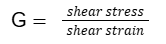
- Q11: State Hook's Law.Ans: Hook's Law states that:
“Within elastic limits, stress is directly proportional to strain”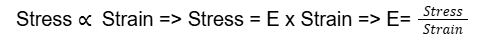
- Q12: Define Tension.Ans: Increase in length is called Tension.
- Q13: Define Compression.Ans: Decrease in length is called Compression.
- Q14: Define Tensile Force.Ans: A force that produces Tension (Increase in length) is called Tensile Force.
- Q15: Define Compressive Force.Ans: A force that produces Compression (Decrease in length) is called Compressive Force.
