DESIGN OF BEAM & LINTEL
Other Chapters
STRESSSTRAINELASTICITYCENTER OF GRAVITYMOMENT OF INERTIASHEAR FORCE & BENDING MOMENTSOIL MECHANICSDEFLECTION IN BEAMSDESIGN OF BEAM & LINTELDESIGN OF RCCDESIGN OF RCC COLUMN & FOOTINGDESIGN OF RCC STAIRS
- Q1: Define beam.Ans: A beam is a horizontal structural element that resists loads applied perpendicular to its axis, primarily by bending.
- Q2: What is meant by lintel?Ans: A lintel is a horizontal structural member placed over door and window openings to support the wall above.
- Q3: Define moment of resistance of beam.Ans: Moment of resistance is the maximum moment that a beam section can resist without failing, based on its material and cross-sectional properties.
- Q4: Define bending moment.Ans: Bending moment at a section is the algebraic sum of the moments of all external forces acting to one side of that section.
- Q5: Define shear force.Ans: Shear force at a section is the algebraic sum of all vertical forces acting on one side of the section.
- Q6: Define effective span of beam.Ans: The effective span of a beam is the center-to-center distance between two supports or the clear span plus the effective depth of the beam.
- Q7: Define permissible stress of concrete.Ans: Permissible stress of concrete is the maximum stress allowed in concrete under service loads without causing failure or excessive deformation.
- Q8: Define ultimate stress of concrete.Ans: The maximum stress that the concrete can carry without failure is ultimate stress.
- Q9: Define neutral axis of beam.Ans: The neutral axis of a beam is the axis within the cross-section where the bending stress is zero during flexure.
- Q10: Define dead load.Ans: Dead load is the permanent static load due to the self-weight of structural and non-structural components of a building.
- Q11: Define live load.Ans: Live load is the moving load applied to a structure, such as the weight of people, furniture, or vehicles. It is the load that keeps on changing.
- Q12: Define wind load.Ans: Wind load is the force by wind pressure on the structure’s surfaces, considered during structural design.
- Q13: Enlist two loads that are considered for RCC design.Ans: Dead load and live load are two commonly considered loads for RCC design.
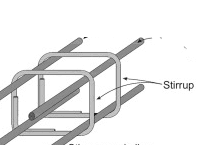
- Q14: What is shear reinforcement?Ans: Shear reinforcement consists of stirrups or bent-up bars provided to resist shear forces and prevent diagonal cracking in beams.
- Q15: Define shear stress.Ans: Shear stress is the internal resistance per unit area developed in a material due to an applied shear force.
- Q16: Define Under Reinforced BeamAns: Such an R.C.C beam in which steel fails before beam failure when concrete may not reach its maximum limit is known as under reinforced beam.
- Q17: Define Over Reinforced BeamAns: Such an R.C.C beam in which concrete fails before the failure of beam when steel may not reach its maximum limit is known as over reinforced beam.
- Q18: Define Balanced BeamAns: A beam in which concrete and steel both remain within their maximum stress limit till the failure of beam is known as balanced beam.
- Q19: Calculate la for (50-1400) concrete.Ans:

- Q20: Define stirrups.Ans: Stirrups are closed-loop steel bars used in reinforced concrete beams and columns to hold the main reinforcement in place and to resist shear and torsional forces.
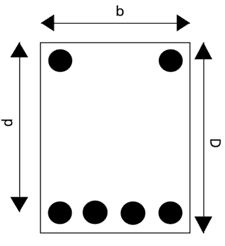
- Q21: Define Singly Reinforced Beam.Ans: A single reinforced beam has reinforcement(steel bars) only at the bottom of the beam to resist the tensile stresses.
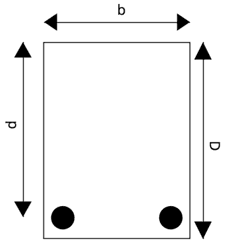
- Q22: Define Doubly Reinforced Beam.Ans: A doubly reinforced beam has reinforcement(steel bars) both at the bottom and top of the beam to resist the compressive and tensile stresses.