CENTER OF GRAVITY
Other Chapters
STRESSSTRAINELASTICITYCENTER OF GRAVITYMOMENT OF INERTIASHEAR FORCE & BENDING MOMENTSOIL MECHANICSDEFLECTION IN BEAMSDESIGN OF BEAM & LINTELDESIGN OF RCCDESIGN OF RCC COLUMN & FOOTINGDESIGN OF RCC STAIRS
- Q1: Define centre of gravity.Ans: The point at which the whole mass of the body appears to be acting is called Centre of Gravity. It is also known as the balancing point of a body.
- Q2: What is centroid?Ans: The centre of any plane figure is called centroid.
- Q3: What is the centroidal axis?Ans: The axis passing through the centroid is called centroidal axis.
- Q4: Define reference axis.Ans: The axis used as a reference for calculations etc. are called reference axis. Example: X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis.
- Q5: What do you know about the axis of symmetry?Ans: The axis that divides the object in such a way that one part is exactly the mirror image of the other part is called the axis of symmetry or symmetrical axis.

- Q6: Define centroidal distance.Ans: The distance from centroid to any point is called centroidal distance.
- Q7: What do you know about composite sections?Ans: Two or more basic shapes combine to form a composite section or a composite figure.
- Q8: Differentiate between symmetrical & unsymmetrical sections.Ans: The sections that when divided from the centroid form two parts that are mirror images of each other, such sections are called symmetrical sections. The sections that when divided from the centroid do not form two parts that are mirror images of each other, such sections are called unsymmetrical sections.
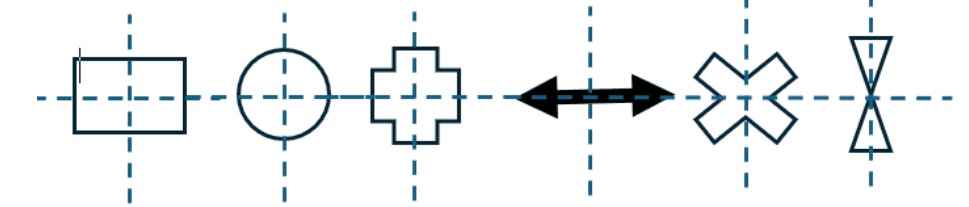
- Q9: Sketch any 6 symmetrical sections.Ans:
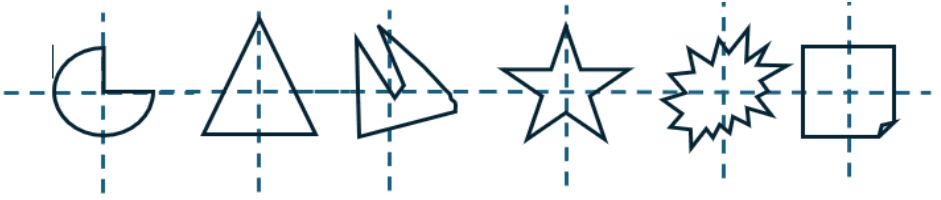
- Q10: Sketch any 6 asymmetrical sections.Ans:
- Q11: Name various methods to calculate centre of gravity.Ans: The methods are:
- ➔ By Moment Area Method
- ➔ By Integration Method
- ➔ By Graphical Method
- ➔ By Geometrical Method
- Q12: What is meant by moment of area?Ans: The product of the area of an object and its centroidal distance is called Moment of Area. Example: “ax” or “ay”.
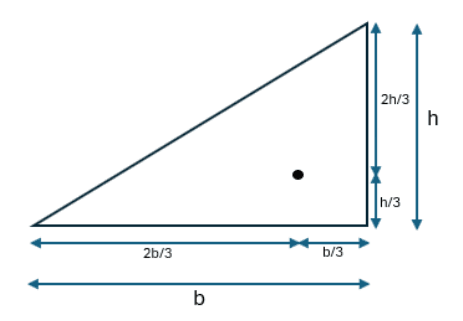
- Q13: Locate the position of the centroid of a right-angles triangle.Ans:
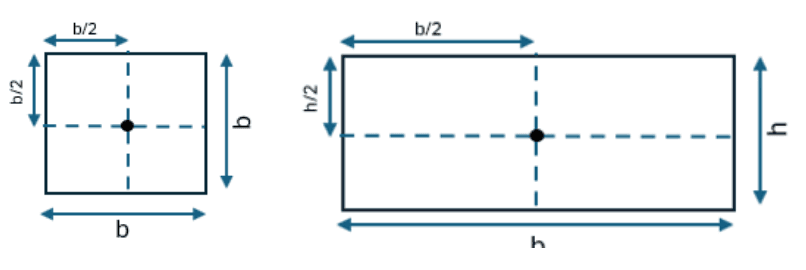
- Q14: Sketch a square and a rectangle and mark the centroids on them.Ans:
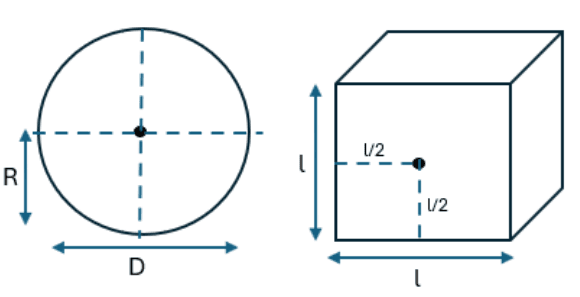
- Q15: Locate the position of the centroid of the circle and cube.Ans:
- Q16: Sketch 4 composite sections.Ans: