STRESS
Other Chapters
STRESSSTRAINELASTICITYCENTER OF GRAVITYMOMENT OF INERTIASHEAR FORCE & BENDING MOMENTSOIL MECHANICSDEFLECTION IN BEAMSDESIGN OF BEAM & LINTELDESIGN OF RCCDESIGN OF RCC COLUMN & FOOTINGDESIGN OF RCC STAIRS
- Q1: Define Force.Ans: A force is a push or pull applied on the body. The unit of force is N.
- Q2: Name the types of stress.Ans: The types are:
- ➔ Direct Stress
- ➔ Tensile Stress
- ➔ Compressive Stress
- ➔ Shear Stress
- ➔ Direct Stress
- Q3: Write down the unit of stress in:Ans:
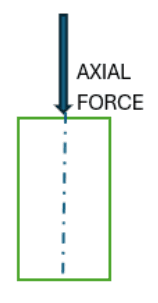
System Measuring Unit MKS kg/m2 CGS g/cm2 FPS lbs/ft2 SI N/m2 - Q4: Define Axial Force.Ans: The force acting at the centroid of an object is called axial force.
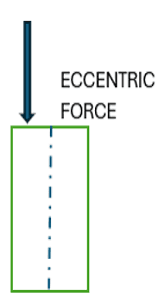
- Q5: Define Eccentric Force.Ans: The force acting away from the centroid of an object is called eccentric force.
- Q6: Define Stress.Ans: The stress produced as a result of shear force is called shear stress. Its formula is:

- Q7: Define Shear Stress.Ans: The stress produced as a result of shear force is called shear stress. Its formula is:
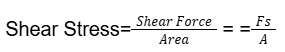
- Q8: Define tensile stress.Ans: The stress produced due to Tensile Force is Tensile Stress.
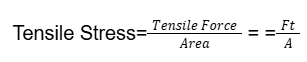
- Q9: Define compressive stress.Ans: The stress produced due to Compressive Force is Compressive Stress.
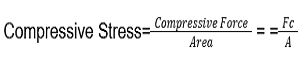
- Q10: Define Bending Stress.Ans: The stress produced by Bending Moment is Bending Stress.
- Q11: Enlist various modes through which forces affect structural members.Ans: Some of the modes are:
- ➔ Tension
- ➔ Compression
- ➔ Shearing
- ➔ Bending
- ➔ Torsion
- Q12: Differentiate between ordinary and pure bending.Ans: A bending moment produced by forces that do not form a couple is ordinary Bending.
The bending moment produced by forces that form a couple is Pure Bending. - Q13: Define Neutral surface.Ans: A neutral surface is the surface of a beam that does not undergo any tension or compression. At this surface, the force and its effects are zero.
- Q14: What do you know about section modulus?Ans: The ratio of Moment of Inertia and distance of extreme fibre from the centroidal axis is section modulus.
- Q15: State any two postulates of bending theory.Ans: Two points are:
- ➔ Beam is straight
- ➔ The material of beam is elastic
- ➔ Hook’s Law is applicable to the material of beam
- Q16: State bending equation.Ans:
 where
where
M = Bending Moment
I = Moment of Inertia
E = Young’s Modulus
R = Radius of Curvature - Q17: Define Direct Force.Ans: A direct force acts normal(perpendicular i.e at 90 degrees) to the object is called Direct Force.
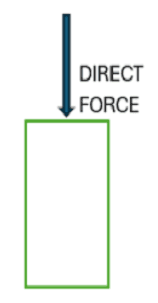
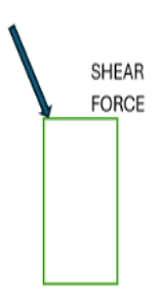
- Q18: Define Shear Force.Ans: A shear force that acts tangent(angle other than 90 degrees) to the object is called Shear Force.