ACOUSTICS
Other Chapters
ACOUSTICSSEWERAGE SYSTEMFIRE PREVENTION & PROTECTIONHEATING, VENTILATION & AIR CONDITIONINGELECTRIFICATION
- Q1: Define Acoustics.Ans: Acoustics is the science of sound, including its production, transmission, and effects in a space.
- Q2: State the principals of sound.Ans: The principals of sound are as follows:
- ➔ Sound is produced by vibrating bodies.
- ➔ Sound requires a medium (air, water, or solid) to travel.
- ➔ Sound travels in waves.
- ➔ Sound can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted.
- Q3: Define Sound.Ans: Sound is a form of energy that is produced by vibrating bodies and is perceived by the ear.
- Q4: How does the ear help in hearing a sound?Ans: The ear detects vibrations in the air and converts them into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound.
- Q5: Define a Vibrating body.Ans: A vibrating body is an object that moves back and forth rapidly to produce sound.
- Q6: Define Acoustics of Sound.Ans: Acoustics of sound is the study of how sound behaves in different environments, including reflection, absorption, and transmission.
- Q7: Define Velocity of Sound.Ans: Velocity of sound is the speed at which sound waves travel through a medium.
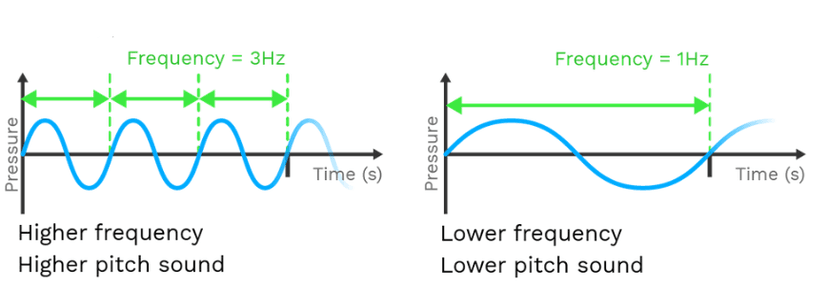
- Q8: Define Pitch of Sound.Ans: Pitch is the quality of sound that tells us how high or low a sound is. It depends on the frequency of the sound wave. Higher frequency means higher pitch.
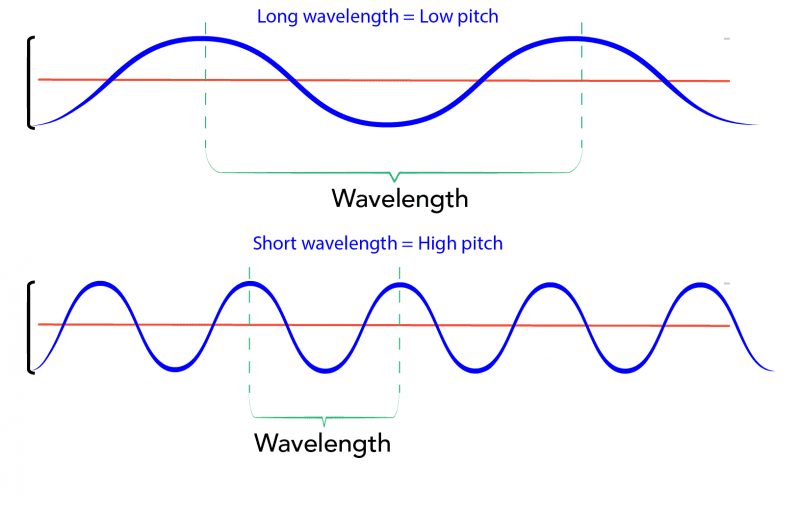
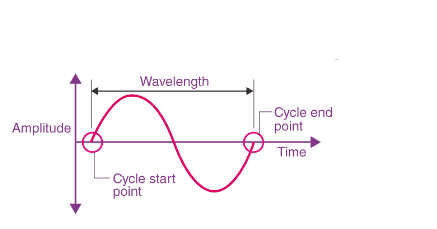
- Q9: Define Wavelength of Sound.Ans: Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions in a sound wave. It is the length of one complete wave.
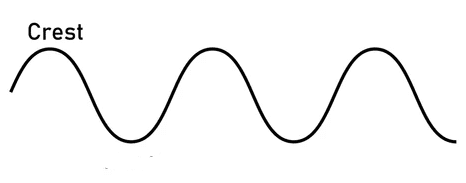
- Q10: Define Crest.Ans: Crest is the highest point of a wave above the rest position.
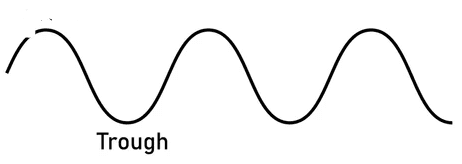
- Q11: Define Trough.Ans: Trough is the lowest point of a wave below the rest position.
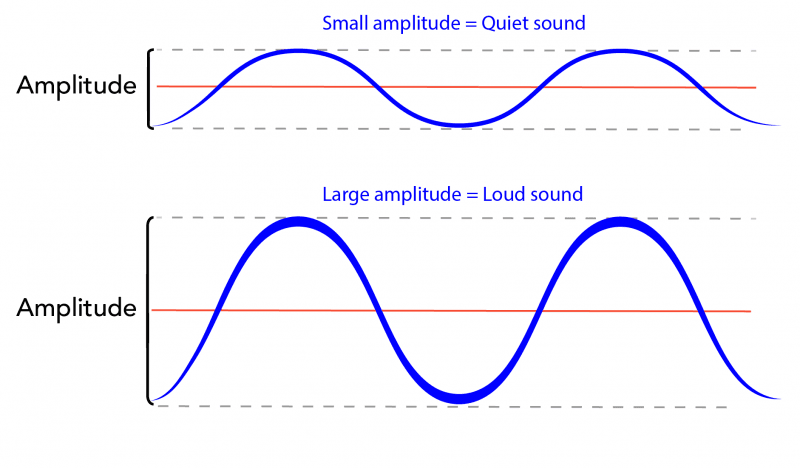
- Q12: Define Amplitude of Sound.Ans: Amplitude is the maximum displacement of particles from their rest position in a sound wave. It determines the loudness of the sound. Greater amplitude means louder sound.
- Q13: Define Intensity of Sound.Ans: Intensity of sound is the amount of sound energy passing through a unit area per second.
- Q14: Define Frequency of Sound.Ans: Frequency of sound is the number of vibrations or cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz).
- Q15: Define Threshold Frequency.Ans: Threshold frequency is the minimum frequency of sound that can be heard by the human ear, which is about 20 Hz.
- Q16: Define Ultrasounds.Ans: Ultrasounds are sound waves with frequencies greater than 20,000 Hz. Humans cannot hear these sounds.
- Q17: Define Infrasounds.Ans: Infrasounds are sound waves with frequencies less than 20 Hz. Humans cannot hear these sounds.
- Q18: Define Reverberation.Ans: Reverberation is the continued sound in a room caused by echoes bouncing off walls after the original sound stops.
- Q19: Define Echo.Ans: Echo is the reflection of sound that is heard distinctly after the original sound.
- Q20: Write two methods of transmission of sound.Ans: The two methods of transmission of sound are:
- ➔ Air borne sound
- ➔ Structure borne sound
- Q21: Define Air Borne Sound.Ans: Air borne sound is sound that travels through the air from a source to a listener.
- Q22: Define Structure Borne Sound.Ans: Structure borne sound is sound that travels through solid materials like walls, floors, or ceilings.
- Q23: Define Sound Absorbing materials.Ans: Sound absorbing materials are materials that reduce the reflection and reverberation of sound in a space.
- Q24: Name 4 Sound Absorbing materials.Ans: Following are some of the sound absorbing materials:
- ➔ Wool
- ➔ Cork
- ➔ Acoustic foam
- ➔ Fibreglass
- Q25: Write 4 properties of Sound Absorbing materials.Ans: Some of the properties of sound absorbing materials are as follows:
- ➔ Porous and soft
- ➔ Lightweight
- ➔ High absorption coefficient
- ➔ Reduces echoes and reverberation
- Q26: Define Decibel.Ans: Decibel (dB) is a unit used to measure the intensity or loudness of sound.
- Q27: How do curtains help in sound absorbing?Ans: Curtains absorb sound waves and reduce echo and noise inside a room.
- Q28: Define Sound Insulation.Ans: Sound insulation is the prevention of sound from passing through walls, floors, or ceilings.
- Q29: Name 4 sound insulating materials.Ans: Some of the sound insulating materials are as follows:
- ➔ Brick
- ➔ Cork
- ➔ Concrete
- ➔ Gypsum
- Q30: Write 4 methods of sound insulation in buildings.Ans: Following are the methods of sound insulation in buildings:
- ➔ Use of double walls
- ➔ Floating floors
- ➔ Discontinuous construction
- ➔ Use of soundproof doors and windows
- Q31: Define Floating floors.Ans: Floating floors are floors separated from the main structural floor by insulation materials to reduce sound transmission.
- Q32: How should rooms be planned for sound insulation?Ans: Rooms should be planned with thick walls, proper spacing, and insulation to minimize noise from outside and between rooms.
- Q33: Explain the acoustic design of auditoriums.Ans: Acoustic design of auditoriums ensures clear sound distribution, proper reverberation, minimal echo, and comfortable listening for the audience.
- Q34: Name the factors affecting the design of auditoriums.Ans: Following factors affect the design of auditoriums:
- ➔ Shape and size of the auditorium
- ➔ Materials used on walls and ceiling
- ➔ Seating arrangement
- ➔ Sound reflection and absorption
- Q35: Define the Silence zone.Ans: Silence zone is the area in a building where noise is minimized, ensuring quiet and comfort.
- Q36: Define Absorbing Co-efficient of sound.Ans: The absorbing coefficient of sound measures how much sound a material can absorb, ranging from 0 (no absorption) to 1 (total absorption).
- Q37: What is Double wall construction?Ans: Double wall construction uses two parallel walls separated by a gap to reduce sound transmission.
- Q38: What is Floating Floor construction?Ans: Floating floor construction uses a floor separated from the main structure with insulation to reduce sound vibration.
- Q39: What is Box type construction?Ans: Box type construction encloses a room within walls, ceiling, and floor filled with insulating materials for soundproofing.
- Q40: What is Discontinuous construction?Ans: Discontinuous construction uses gaps or breaks in walls or ceilings to prevent sound from traveling directly through the structure.
- Q41: Define Cavity wall.Ans: A cavity wall is a wall made of two layers of masonry separated by an air gap to improve sound and thermal insulation.
- Q42: How cavity walls help in sound insulation?Ans: Cavity walls reduce sound transmission by trapping sound in the air gap between the two layers of masonry.
