MATERIAL STATEMENT
Other Chapters
UNITSBUILDING SPECIFICATIONSBILL OF QUANTITITESMATERIAL STATEMENTMARKET RATE SCHEDULESCHEDULES OF BARSESTIMATIONRATE ANALYSIS
- Q1: Define Material Statement.Ans: It is a tabular format that contains a list of all the materials used for a particular project.
- Q2: What is the importance of preparing a material statement?Ans: Material Statement is prepared for:
- ➔ Providing a record
- ➔ Improving Efficiency
- ➔ Maintaining Quality
- Q3: Write the number of bricks required for 100cft brick masonry?Ans: The number of bricks for 100cft brick work is 1350.
- Q4: State the thickness of plaster used for flush pointing and struck pointing.Ans: For Flush pointing thickness is ¼” and for struck pointing thickness is ½”.
- Q5: State the difference between flush pointing and deep struck pointing.Ans:
Deep Struck Pointing is recessed from the wall surface, creating a shadow effect.
Flush Pointing is level with the wall surface, giving a smooth, uniform look. - Q6: Name various materials required for concrete work.Ans: The materials are:
- ➔ Cement
- ➔ Sand
- ➔ Aggregate
- ➔ Water
- Q7: How much labor will be required for 500c.u.m concrete work.Ans: Labor = 6
Mason = 1
Waterman = 1/2 - Q8: Draw a rough sketch of Material Statement.Ans:

- Q9: Calculate dry material for 100c.u.m cement concrete 1:2:4Ans:

- Q10: Calculate dry concrete for 500cubic meter wet concrete.Ans:

- Q11: Calculate dry mortar for 500c.u.m wet cement mortar.Ans:
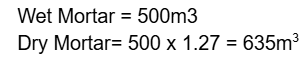
- Q12: Write the number of bricks required for 500c.u.m dry brick masonry.Ans:
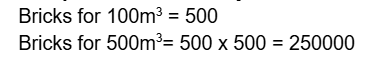
- Q13: Calculate dry material for 500cft ¾” thick plaster work 1:3Ans:

